
(New York Times) – Fitness is full of numbers meant to help you become faster and stronger. There’s your mile run time, your resting heart rate and measures of strength and flexibility. But perhaps the gold standard is VO2 max.
A handful of years ago, the test — which tracks how much oxygen your body absorbs — was an obscure tool mainly used by elite athletes. Today, it’s touted by fitness professionals and wellness experts like Peter Attia as being a useful measure for all exercisers. [Click here for full article]
Synopsis
VO2 max is a measure of the maximum amount of oxygen your body can use during intense exercise, indicating your aerobic capacity and overall fitness. It is expressed as milliliters of oxygen consumed per minute per kilogram of body weight. While traditionally used by elite athletes, it’s now considered valuable for anyone interested in health and longevity. Accurate measurement typically requires an expensive and exhausting lab test, but wearables can provide estimates. A high VO2 max is linked to longer lifespan and better health, and regular testing can help monitor and improve fitness levels. For those who can’t access lab tests, setting and achieving performance goals is a practical alternative.
Articles
- [Principal Article]
This Test Might Be the Best Way to Track Fitness and Longevity (New York Times, Talya Minsberg, April 11, 2024) - How does VO2 max correlate with longevity? (peterattiamd.com, Peter Attia, May 17, 2022)
- Heart Rate – Exercise Basics (over50longevity.com, Michael OConnor, August 6, 2024)
Notes
The simplest formula to calculate VO2 max is VO2 max = 15 x (HRmax/HRrest). Calculate your max heart rate by subtracting your age from 220 and then divide that result by your resting heart rate. I usually take my resting heart rate from my Apple Watch Health app but it can be calculated manually upon awakening in the morning and counting the number of heart beats over 60 seconds taken from the carotid artery. Once you have that quotient (the result of max heart rate divided by resting heart rate) you will times it by 15. The result will by an approximation of your VO2 max.
For example, my formula looks like this … (biological male, 56 years of age)
- Max Heart Rate = 164 BPM (220-56)
- Resting Heart Rate = 46 BPM
- VO2 max = 15 x (164/46)
- VO2 max = 15 x 3.56521739
- VO2 max = 53
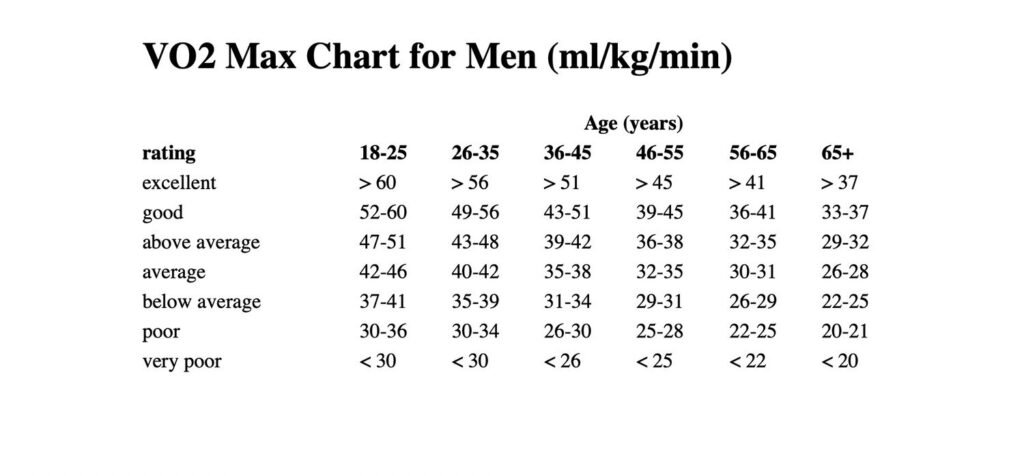
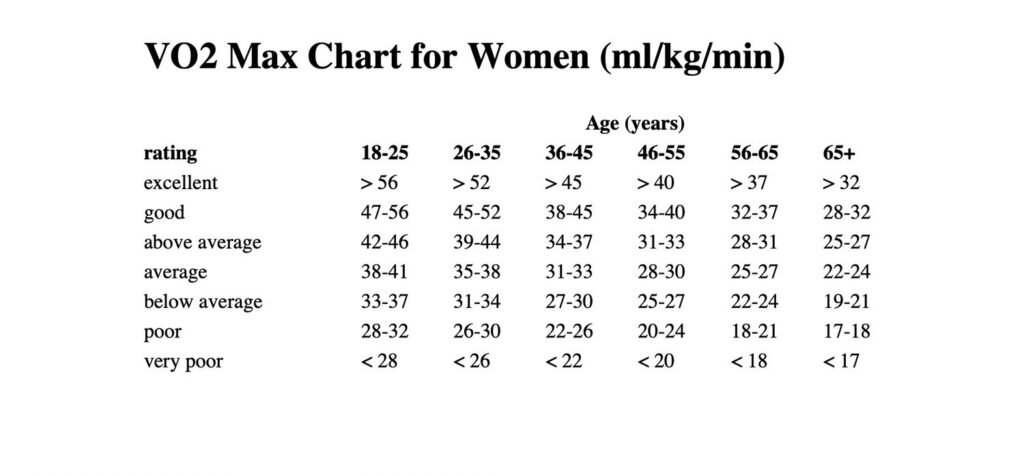
The charts below are VO2 max ranges for biological males and females


Leave a Reply